Absolute Pressure vs Gauge Pressure vs Differential Pressure Measurements
Choosing the right pressure reference
1. Which is the pressure formula? How do you convert pressure to force?
This article shows the difference between the different types of pressure.
Pressure is one force per unit area and can be expressed in units such as pascal, bar, atmospheres, kilograms per square centimeter, and psi.
Any good instrumentation technician needs to know the difference between the basic types of pressure measurement.
Pressure, in addition to being one of the most widely used variables in process control, is undoubtedly the most important. Pressure is a measure in itself and because other important variables such as flow, density and level can be deduced from it. Pressure is a measure that represents about 25% of the sales volume of the global market for measuring instruments.
Pressure formula may be expressed as a force per unit area or in terms of liquid column height.
The expression pressure = force / area shows that o tremendous force will exist for a nominal pressure, provided the area is large, also a large pressure is produced by o small force when the effective area is small.

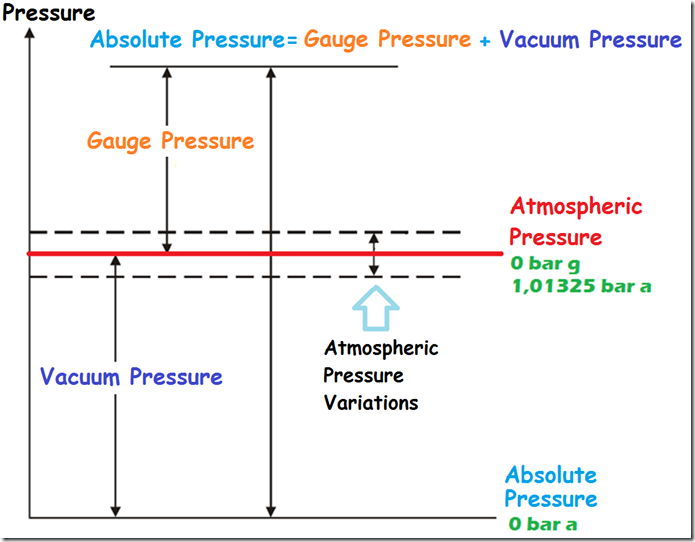
Pressure can have one of two reference points: atmospheric pressure or absolute zero pressure. A pressure measurement using atmospheric pressure as the reference point is known as gage pressure (bar g). The pressure measurement referencing absolute zero pressure is known as absolute pressure (bar a).
The pressure measurement can only be performed by comparing a known or reference pressure measurement and another unknown pressure measurement that we wish to measure.
The following video will show an small introduction to pressure measurement.
2. Atmospheric Pressure
2.1 What is Atmospheric Pressure?
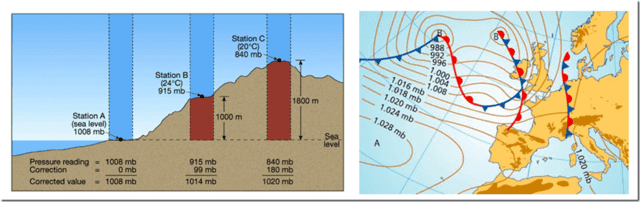
- This is the pressure experienced on the earths surface where each square meter supports a column of air, giving a pressure of 1013 mb. The pressure reduces progressively towards the top of the column. This is illustrated by the difference between pressure at sea level and that at the top of a high mountain. It varies due to changes in temperature and climatic conditions.
- It is caused by the weight of the atmosphere. It depends on the climatic changes, the reference pressure is the pressure at sea level which is equal to 1013 mbar or 760 mmHg.
- It is the most important pressure measure for the life of humans on earth. It is identified by the abbreviations amb (amb = environment, surrounding).
- This pressure is produced by the weight of the air gas contained in the atmosphere surrounding the earth. The size of this gas column ranges from the earths surface to an altitude of about 300 kilometers. As we approach the distance of 300 km from the earths surface the atmospheric pressure decreases steadily until practically equals zero (complete vacuum).
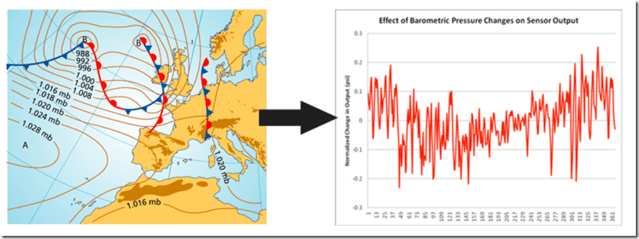
- Due to climatic changes the atmospheric pressure of air undergoes variations, these variations are not very significant, in terms of pressure, and can be observed in the thousands of daily meteorological reports.
- At sea level, atmospheric pressure has an average value of 29.90 inches of Mercury or 760 mm Hg absolute (mercury column), according to the Torricelli experiment. The fluctuation of the atmospheric pressure due to the climatic changes can be around 5%. The value of this pressure decreases as altitude increases.
- It can have a variation of ± 200 mbar depending on the height above the sea level, and variation of ± 30 mbar per day depending on weather conditions.

- Physical Properties of U.S Standard Atmosphere:
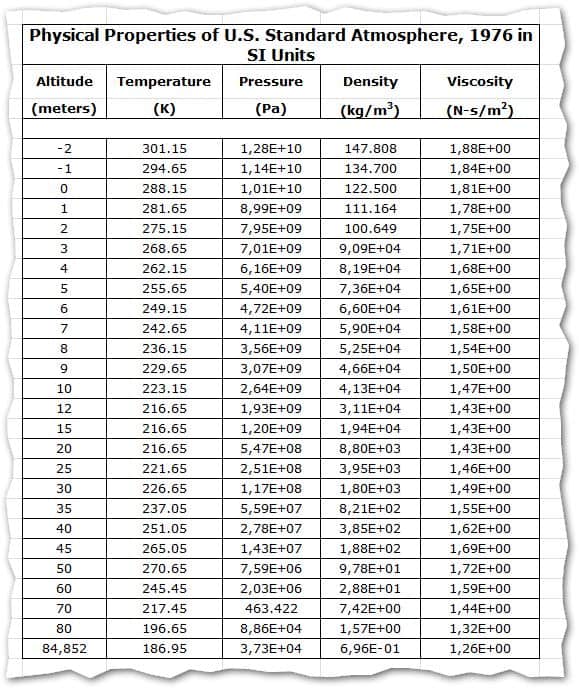
Basic Assumptions:
Air is a clean, dry, perfect gas mixture; Specific heat ratio = 1.40; Molecular weight to 86 km = 28.9644 Principal sea-level constituents:
Principal Sea-Level Constituents:
- N₂: 78.084%
- O₂: 20.9476%
- Ar: 0.934%
- CO₂: 0.0314%
- Ne: 0.001818%
- He: 0.000524%
- CH₄: 0.0002%
3. Absolute Pressure
3.1 What is Absolute Pressure?
- Absolute zero pressure is the ultimate reference point. This pressure is the pressure of empty space in the cosmos.
- The absolute pressure definition measurement is based on the absolute zero pressure measurement as a reference measure.
- It can be recognized by the subscript abs. Another way to define it is add to the atmospheric pressure the value of pressure gauge taken from the instrumentation. The absolute pressure measurement is indicated by the letter a or the abbreviation abs in order to distinguish it from the other types of pressure (relative pressure, differential pressure).

3.2 How to find Absolute Pressure?
- The origin of the suffix comes from Latin: absolutus = independent or separated from.
- It is defined as the pressure referred to absolute zero pressure or a perfect vacuum. The best example of an absolute referenced pressure is the measurement of barometric pressure.
Absolute pressure definition measuring instruments are normally used to measure barometric pressure or altimeters. For this type of applications it is necessary to have constant reference pressure. For this reason the atmospheric pressure can not be used.
- Always take into account the atmospheric pressure. Then we can say that the measure of absolute pressure definition uses a reference to a perfect vacuum.
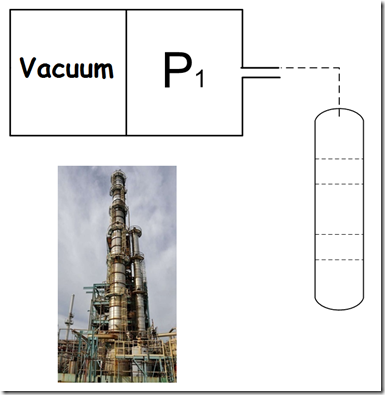
- Therefore this pressure measurement will always take into account the influence of the atmospheric pressure on the final measurement. If the location of the absolute pressure measurement definition changes, especially if it involves elevation changes, this measurement may undergo a change due to changes in the surrounding atmospheric pressure. It is necessary to remember that this measure always takes into account this influence of the atmosphere.
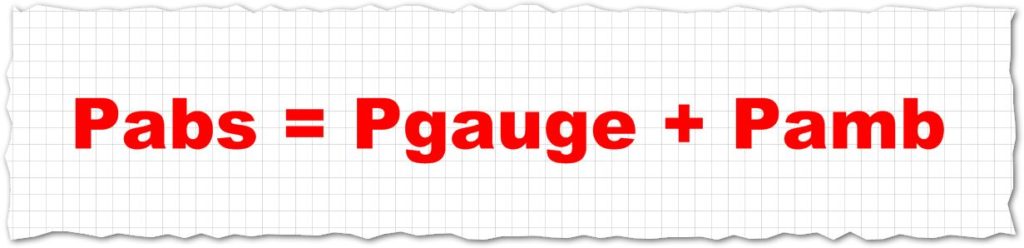
- The formula above presents the relation between absolute pressure and pressure gauge.
- The absolute pressure measurement will always be positive.
- This type of measurement is usually more expensive than the relative pressure or pressure gauge.
- The measurement of static pressure in a reservoir containing oil or gas as well as all calculations and analyzes are performed taking into account in absolute pressure.
3.3 Absolut Pressure Applications
- Applications where high accuracy of vacuum measurement is required.
- Control applications where low pressure or vacuum is needed. In these applications it is necessary to have a measure that takes into account the influence of atmospheric pressure.
- Measurement of low pressure in the distillation vacuum columns.
- Vacuum Reactors
- Leakage control in tanks and circuits
4. Gauge Pressure
4.1 What is Gauge Pressure?
- Gauge or relative pressure (Pg or Prel) is the most common pressure measurement. Basically we can define it as the pressure difference between the pressure that we want to measure and the pressure of the environment. It is the pressure measured with reference to atmospheric pressure. Represents the difference between the measured pressure and the actual atmospheric pressure. As the actual atmospheric pressure is variable, the comparison of measured values in different time intervals is uncertain.
- Usually the term pressure without adjectives is used to refer to a measure of positive pressure greater than atmospheric pressure.

- In order to be able to distinguish the absolute pressure definition from the gauge pressure definition we must add the suffix abs to the letter P (Pabs) to be able to refer to the absolute pressure.
- It depends on an element that measures the difference between absolute pressure and atmospheric.
Does not take into account the effect of atmospheric pressure.
- It can be recognized by the subscript reg or g (gauge).
- They constitute 95% of the types of meters installed in the chemical industry.
- It can be positive (P1> Patm) or negative also known as vacuum (P1< Patm)
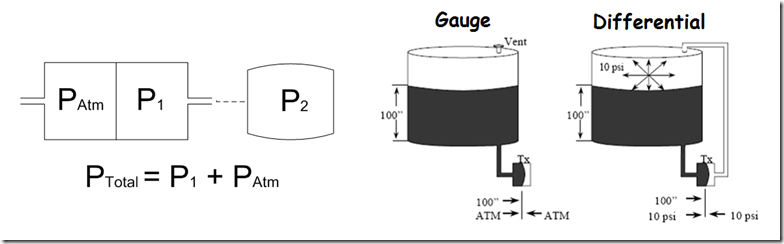
- The gauge pressure always measures the pressure with respect to the atmospheric pressure around the pressure transmitter.
- The pressure transducer has a sensing element sensitive to changes in pressure. Due to the linearity of the instrument or pressure sensor it is possible to relate a given deflection to a defined pressure.
- To carry out the measurement of relative pressure or gauge it is necessary that the pressure transmitter have some type of ventilation that allows to put the instrument in contact with the atmosphere.
- Ventilation is used to take the atmospheric pressure as a reference point.
- An advantage of the relative pressure measurement is that regardless of the location of the Earth where the measurement is installed it will always be independent of the atmospheric pressure.
- The relative pressure measurement always uses ambient atmospheric pressure as the reference pressure.
4.2 Gauge Pressure Applications
- Measurement of level in atmospheric tanks.
- Measurement of Pressure in pipes and tanks where working pressure is greater than the variations due to atmospheric pressure. The change in atmospheric pressure have no impact in the final pressure measurement.
- Measurement of pressure in air conditioning and air control and corrosive gases. For example in lab rooms.
Watch the following video from VEGA which explains the difference between Absolute Pressure and Gauge Pressure:
5. Differential Pressure
5.1 What is Differential Pressure?
- It is defined as the difference between two pressures, also known as dP, loss, etc ...
- It is also defined as the difference between a certain pressure value and another used as a reference. In a sense, absolute pressure could be considered as a differential pressure that takes absolute vacuum as a reference and relative pressure as another type of differential pressure that takes atmospheric pressure as a reference.
- The differential pressure measurement may be a little more complex than the relative pressure measurement or the absolute pressure definition measurement, although it is simply used to measure two different media.

- It does not take into account the effect of atmospheric pressure.
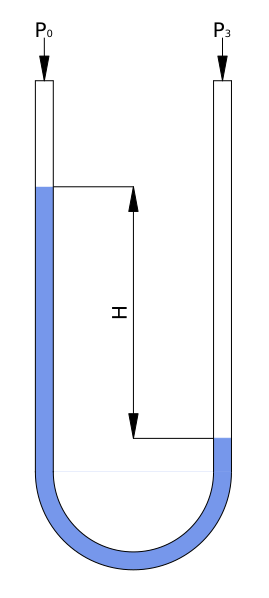
Although most relative pressure measurements are technically identical to a differential pressure measurement instrument, the differential pressure measurement instrument is not referenced to the atmospheric pressure measurement, but we use this measuring chamber to connect it to a medium that we want to measure. In this way, by numerical difference between the two pressure measurements of the 2 chambers we obtain the differential pressure measurement.
- The differential pressure measurement is used to check the drop or loss of pressure from one side of an object to the other side.
- Vacuum pressure: The term vacuum is used if the pressure is below atmospheric pressure.
5.2 Differential Pressure Applications
- Level measurement in tanks and vessels
- Density measurement
- Flow Measurement
- Interface Level Measurement
- Flooding Monitoring in Distillation Column
- Filter monitoring
- Monitoring pumps and valves
- Fire Monitoring Systems Sprinklers
- Processes where is needed a supply pressure monitoring
6. Pressure Measurement Facts
6.1 When to measure absolute and gauge pressure?
This is not always straightforward but generally if you want to measure or control a pressure that is influenced by changes in atmospheric pressure, e.g. the level of liquid in an open tank or the output pressure of an air compressor; you would use a vented gauge pressure transmitter since you are interested in the pressure reading minus the atmospheric pressure component.
If you want to measure pressures that are not influenced by changes in atmospheric pressure, e.g. leak testing a completely sealed non-flexible container, you would use an absolute pressure sensor. If a gauge pressure sensor was used instead to measure the container pressure, and the barometric pressure changed, then the sensors reading would change, despite the fact that the pressure in the container remains the same.
The use of gauge pressure is extremely important in industry, since it is a measure of the stress within a vessel and the tendency of fluids to leak out.
6.2 What instrument is used to measure air pressure?
The Barometer is the instrument used to measure air pressure.